-
머신러닝의 개념과 용어AI 2019. 12. 9. 14:09
Machine Learning
- What is Machine Learning
* Limitations of explicit programming : Spam filter, Automatic driving
- Supervised / Unsupervised Learning
* Supervised Learning (지도 학습)
# 라벨링되어있는 데이터(training set)를 학습하는 방식으로 가장 일반적인 ML 학습 방식
# EX) Image Labeling, Email spam filter, Predicting exam score
# Type of supervised Learning
Regression 예측에 대한 결과값이 범위에 해당하는 값일 경우 공부 시간을 기반으로 한 기말고사 점수 예측 : 결과값 ( 0 ~ 100 ) Binary Classification 예측에 대한 결과값이 Yes Or No와 같은 이분화된 라벨일 경우 공부 시간을 기반으로 한 시험 Pass/Fail 예측 : 결과값 ( Pass Or Fail ) Multi-label Classification 예측에 대한 결과값이 여러개의 라벨이 될 수 있을 경우 공부 시간을 기반으로 한 학점 예측 : 결과값 ( A or B or C or F ) * Unsupervised Learing
# 라벨링되어있지 않은 데이터들을 이용하여 학습하는 방식 : Google News Grouping, Word clustering
Tensorflow
- 구글에서 개발한 Open Source Software Library for Machine Intelligence
- Tensorflow 외의 오픈소스 딥러닝 라이브러리 : Caffe, Keras, mxnet, Theano 등...
- Python library for numerical computation using data flow graphs
- What is a Data Flow Graph?
* Graph = 노드와 노드 간의 연결인 엣지로 구성된 것
* Node in Data Flow Graph = Operation
* Edge in Data Flow Graph = data arrays = Tensors
hello = tf.constant("Hello, World!") # Create a contant op = Create a Node sess = tf.Session() # Craete Session for Data flow Graph Run print(sess.run(hello)) # run the op and get result# result b 'Hello, World!' # b 'String' 'b' indicates Bytes literals- Tensor, Data, Session
node1 = tf.constant(3.0, tf.float32) node2 = tf.constant(4.0) node3 = tf.add(node1, node2)print("node1: ", node1, "node2: ", node2) print("node3: ", node3) #result node1: Tensor("Const_1:0", ... ) node2: Tensor("Const_2:0", ...) node3: Tensor("Add:0", ...)
Session 실행 전 Data Flow Graph sess = tf.Session() sess.run([node1, node2]) sess.run(node3)
Session 실행 후 Data Flow Graph - Placeholder
* 그래프를 임의로 미리 그려놓고 그래프 실행 단계에서 값을 넣어주고 싶을 경우 사용하는 노드
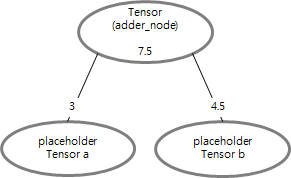
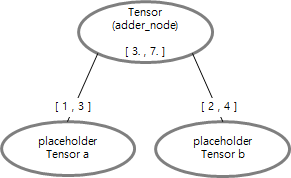
a = tf.placeholder(tf.float32) b = tf.placeholder(tf.float32) adder_node = a + b sess.run(adder_node, feed_dict={a: 3, b: 4.5})) # result : 7.5 sess.run(adder_node, feed_dict={a: [1,3], b: [2,4]})) # result : [3. 7.]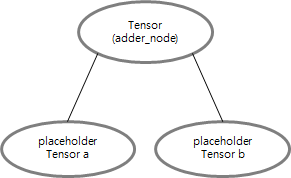
- Tensor Ranks, Shapes, and Types

https://www.tensorflow.org/programmers_guide/dims_types 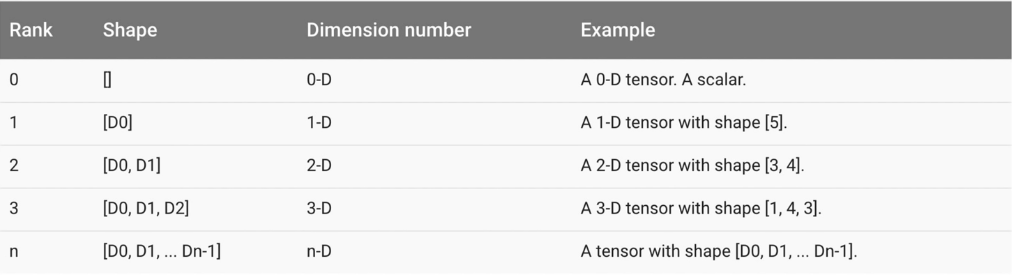
https://www.tensorflow.org/programmers_guide/dims_types 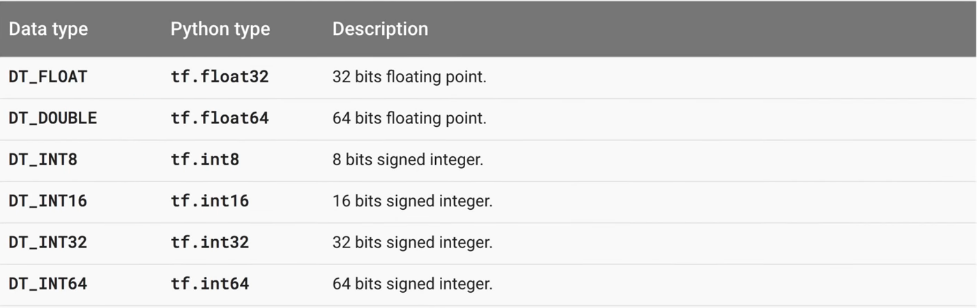
https://www.quora.com/When-should-I-use-tf-float32-vs-tf-float64-in-TensorFlow 이 글은 http://hunkim.github.io/ml/를 학습하며 내용을 정리해놓은 글이다.
'AI' 카테고리의 다른 글
[ML] Logistic Regression (Classification) (0) 2019.12.11 [DL] Neural Nets for XOR (0) 2019.12.11 [ML] Linear Regression (0) 2019.12.11 Nvidia Driver & CUDA install (0) 2019.10.01 Machine Learning (0) 2019.07.16